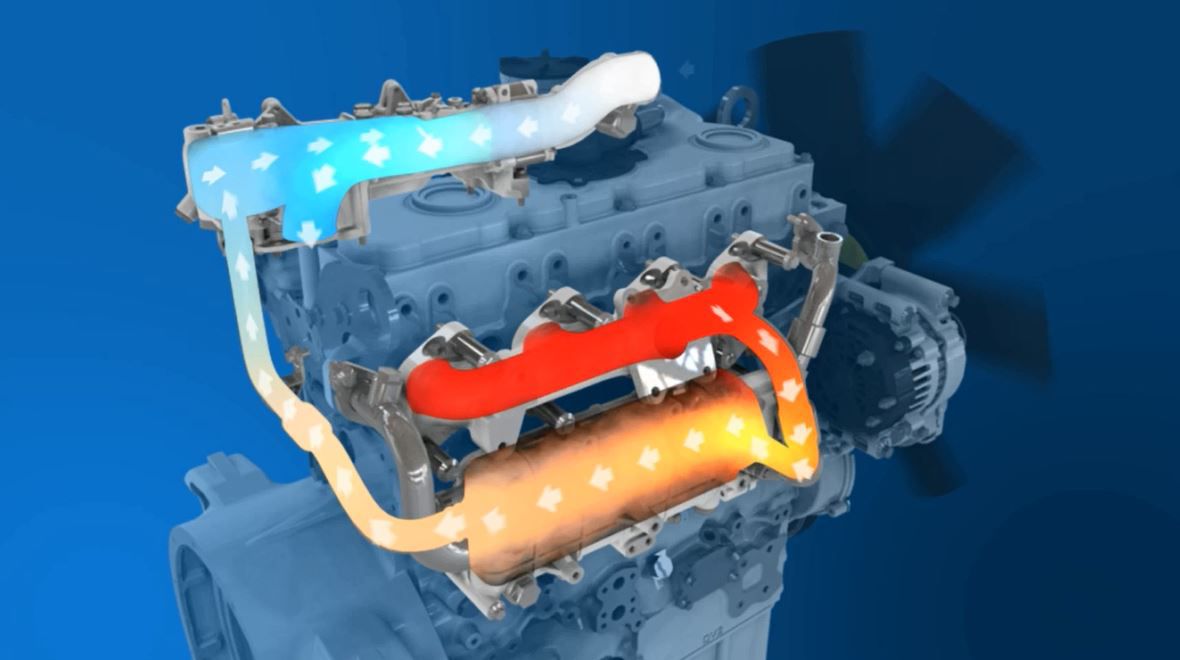
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is used to reduce the levels of NOx emitted by the engine. By recirculating exhaust gases into the engine’s cylinder, a percentage of the air is replaced with CO2. This process lowers the combustion temperature due to the reduced amount of oxygen which, in turn, reduces the amount of NOx formed.
The exhaust gases can either be externally cooled and piped into the inlet manifold or managed internally through the camshaft.

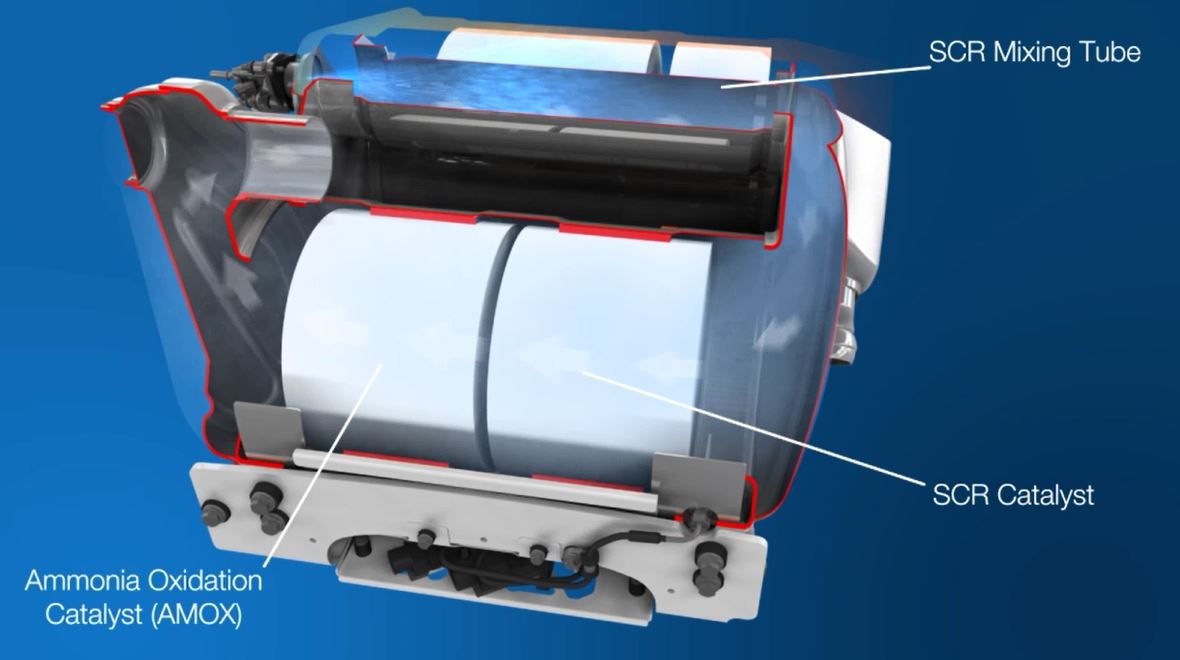
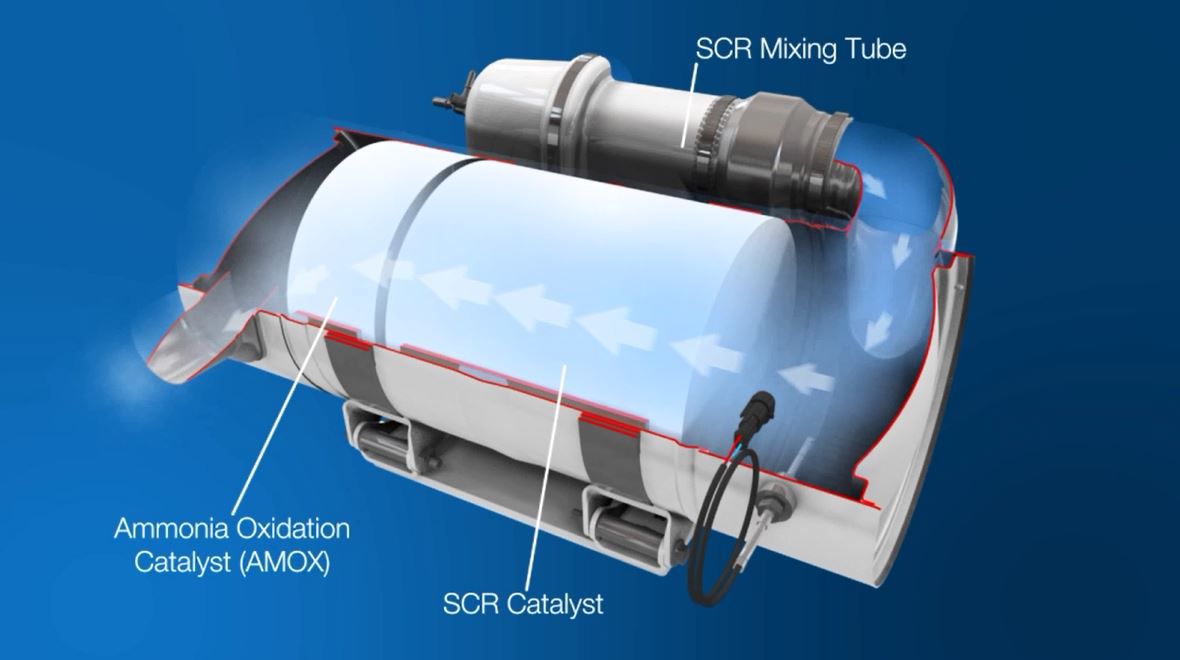
If you’re using a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system you need diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) for the system to work.
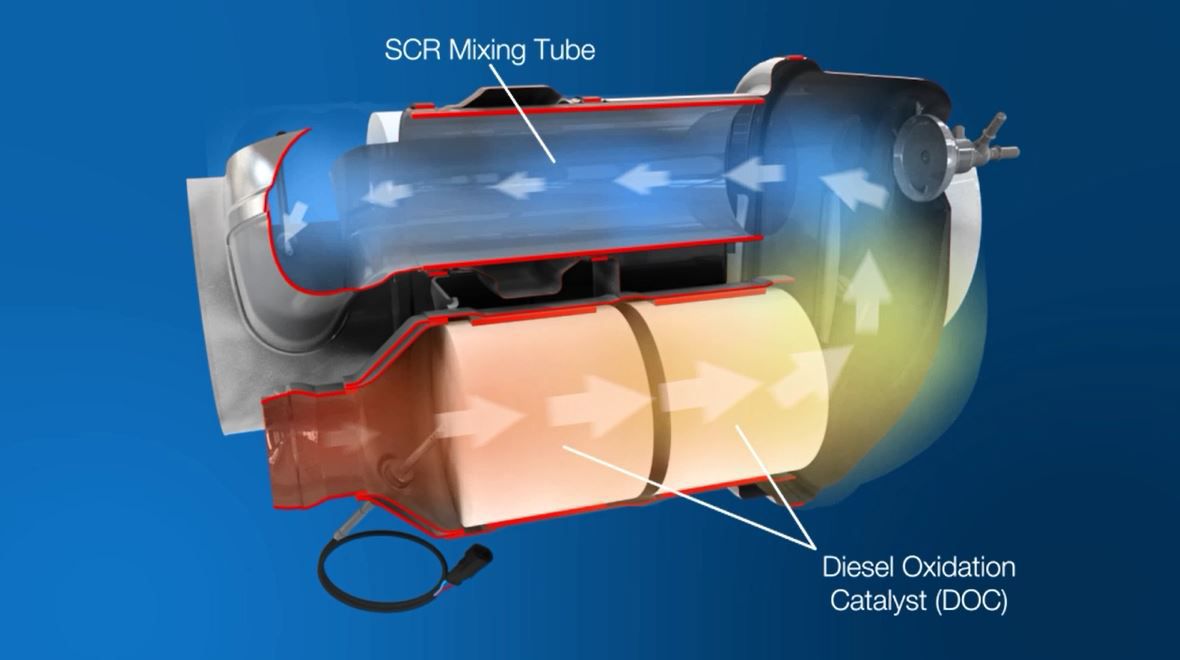
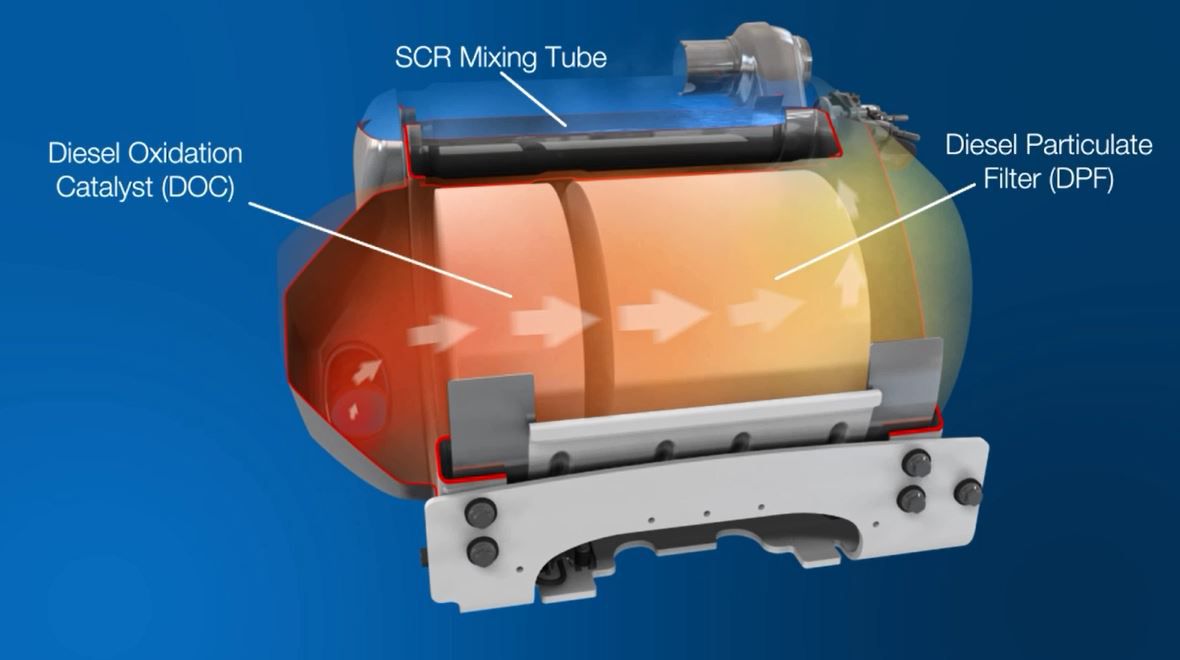
Learn MoreA diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) is an aftertreatment component that is designed to convert carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide and water.
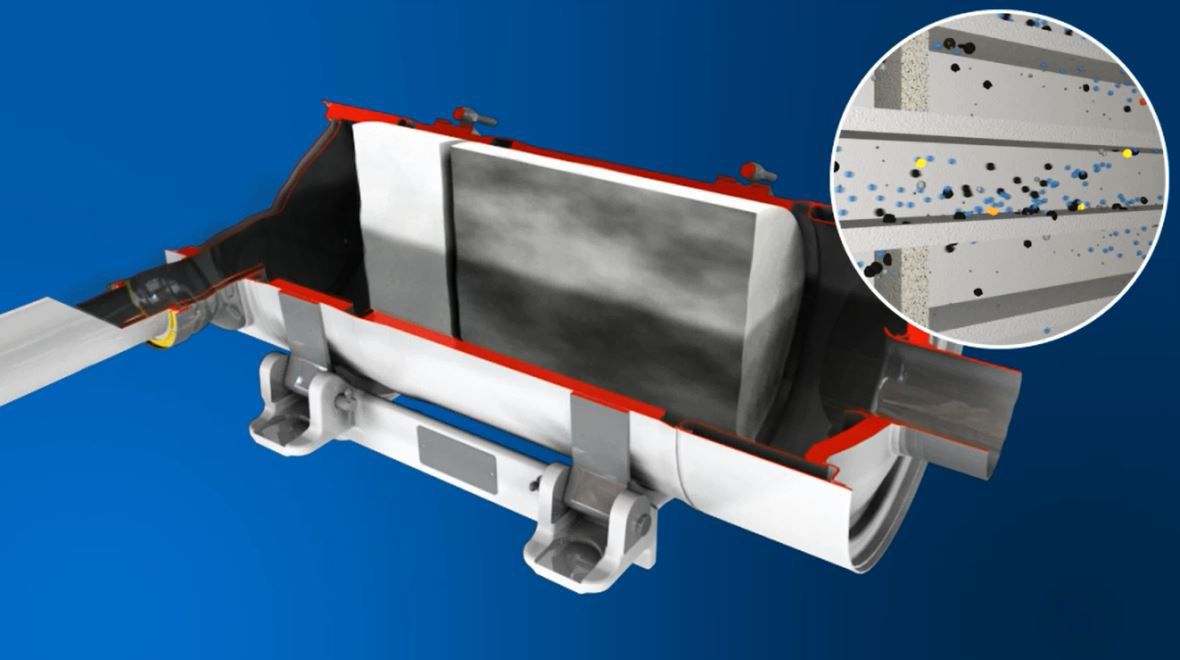
Learn MoreOur diesel particulate filter (DPF) solutions capture a high percentage of particulate matter or soot.
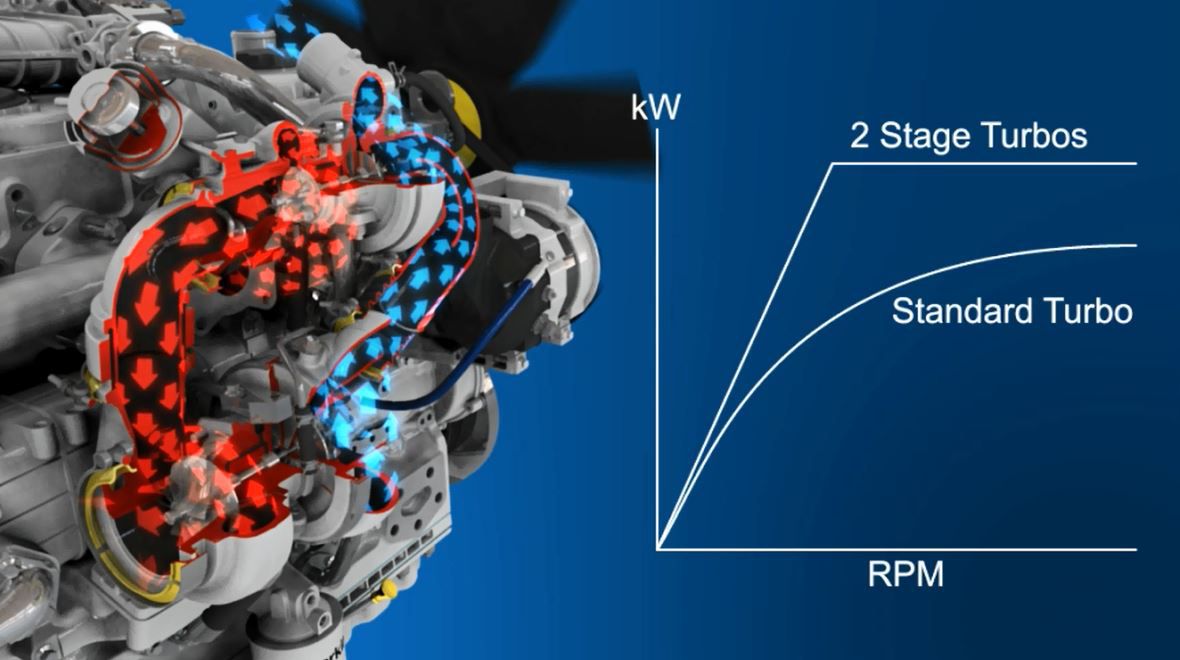
Learn MoreA series turbo set-up involves two turbochargers installed to operate in sequence.
Learn MorePassive regeneration is an approach used to oxidise particulate matter (PM) in the diesel particulate filter (DPF).
Learn MoreOne of the options available for reducing NOx emissions is selective catalytic reduction (SCR), used on a number of our engines.
Learn MoreOne of the technologies available for the reduction of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) is exhaust gas recirculation (EGR).
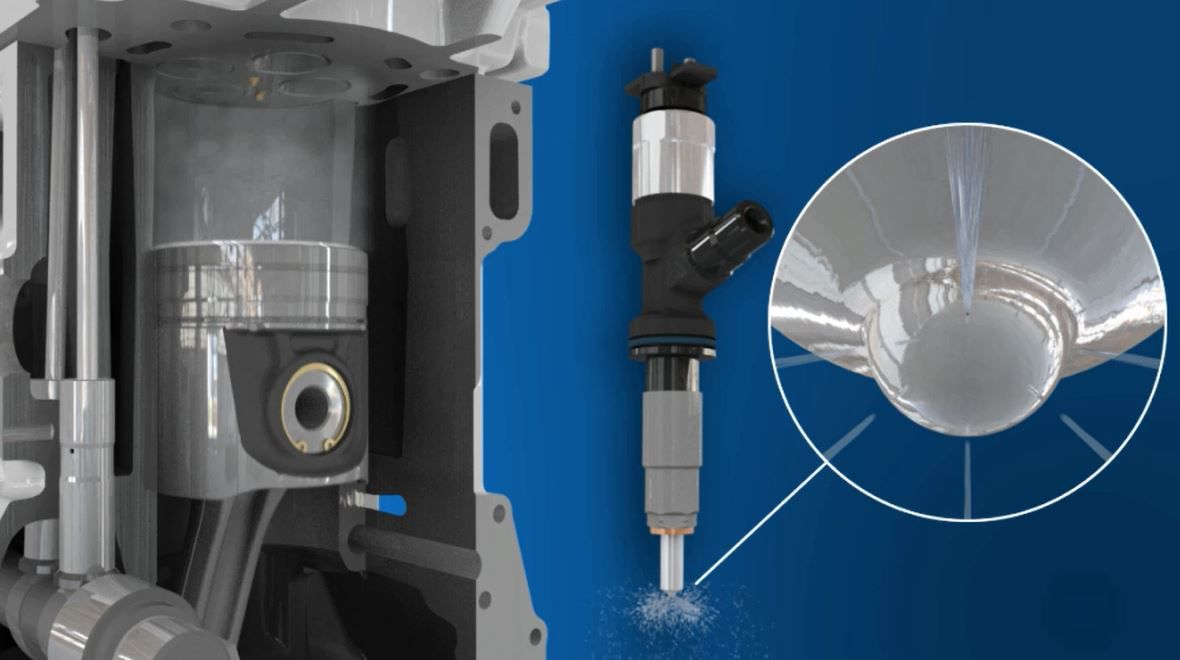
Learn MoreReducing particulates and optimising fuel consumption are primary reasons for adding high pressure common rail to our engines.
Learn MoreIf you're ready to receive trusted advice from a Perkins expert, speak to our team today.
Connect with usOur digital magazine with the latest news, interviews and analysis.
Read moreYour regional Perkins Distributor can provide local, on-the-ground engine support.
Learn More