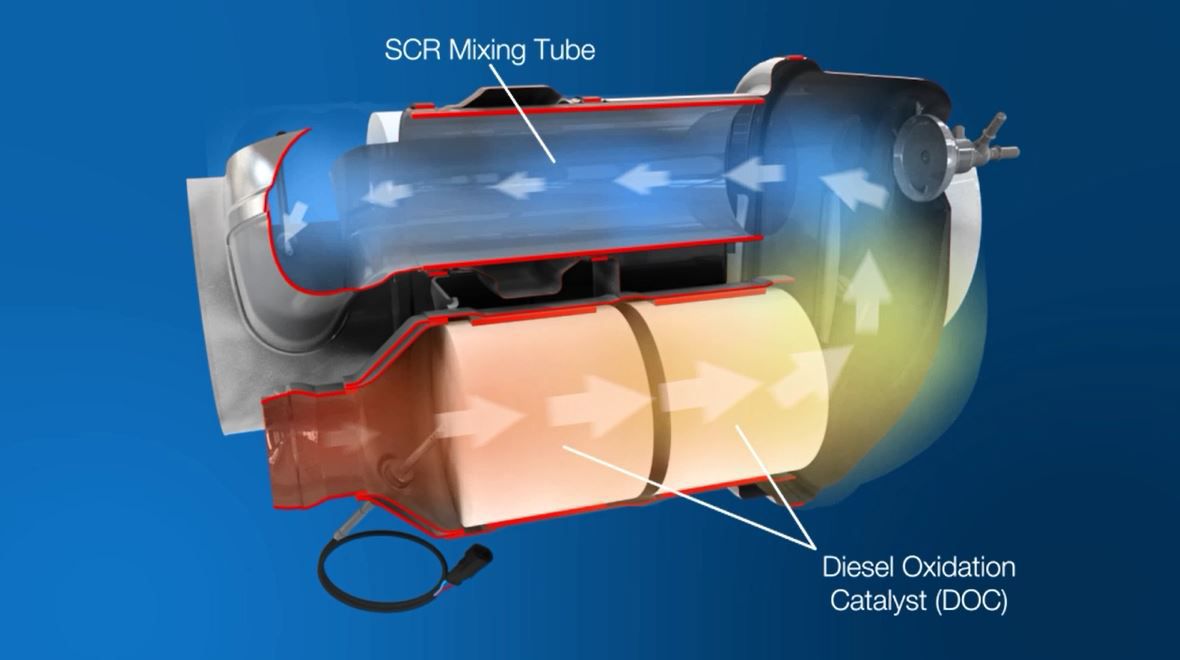
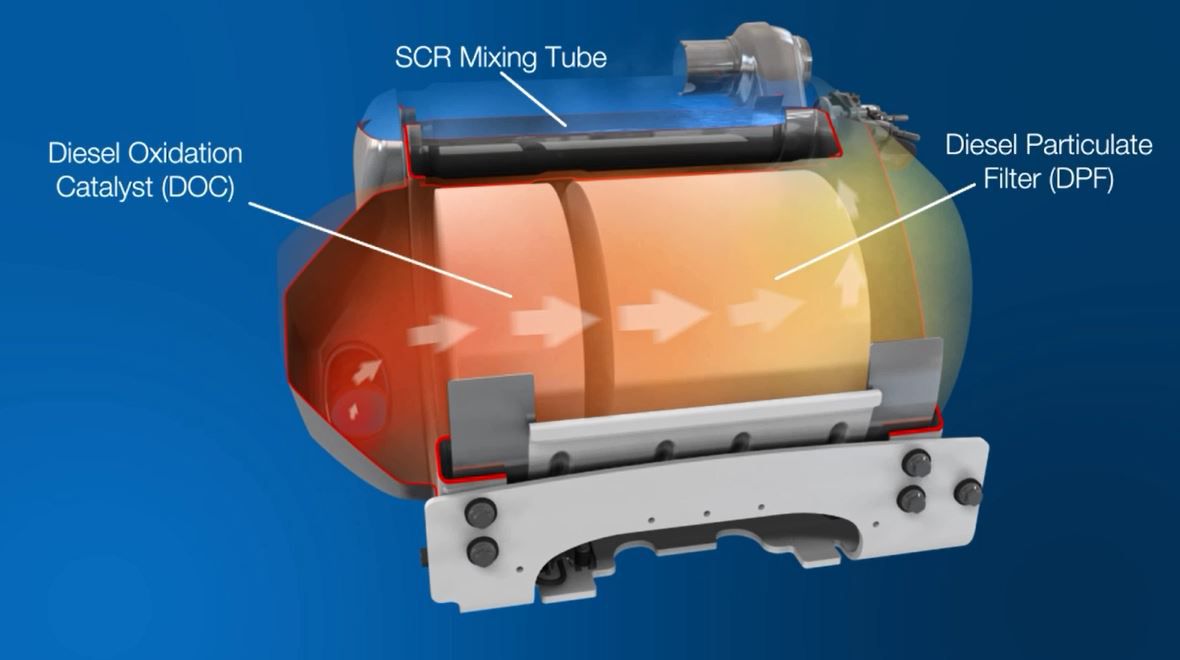
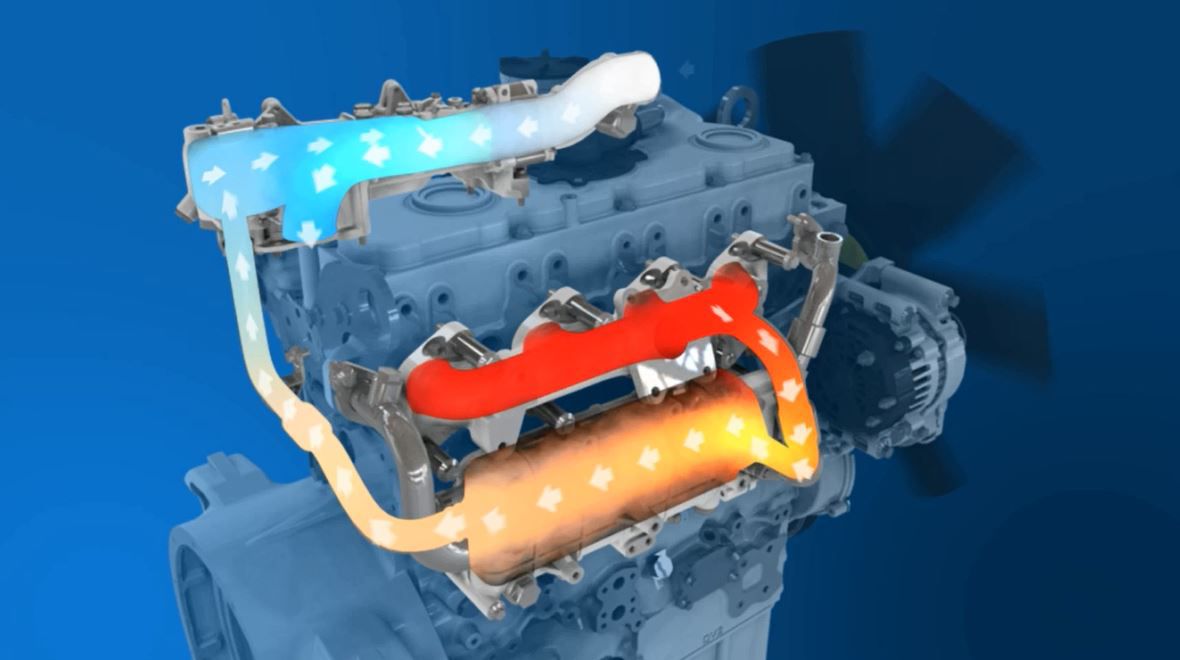
A diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) is an aftertreatment component that is designed to convert carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water. The device is used on all our EU Stage IV/U.S. EPA Tier 4 Final products – from the 400F through to the 1206F.
It doesn’t matter if you are running your diesel engine on the road or off, you must still adhere to strict emissions standards. A diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) is an aftertreatment device that can help you do that, as it effectively turns CO and hydrocarbons into CO2 and water vapour.
The DOC is part of the technology we offer to assist you in meeting Stage IV and Tier 4 Interim/Final emissions standards. It breaks down pollutants in the exhaust stream from a diesel engine, helping to reduce particulate matter (PM). It’s similar to a catalytic converter in a car.
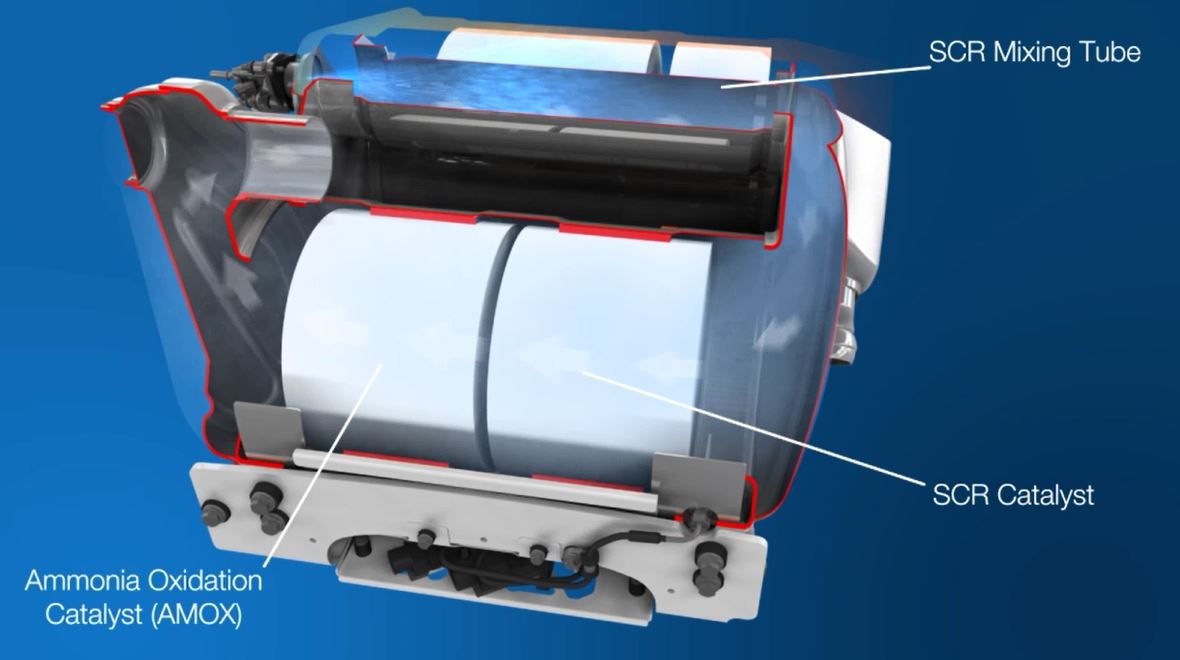
Both carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons are converted in the DOC to carbon dioxide and water vapour. Exhaust gases are optimised so that they can perform in other systems in the aftertreatment, such as the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) or diesel particulate filter (DPF).

Our DOCs provide a simple solution for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). They’re easy to install and maintain and don’t require any additional control from the machine operator.
In many cases, the need for a muffler can be eliminated, and our DOCs can also allow for a wider ratings envelope. Concentrations of NO and NO2 can be optimised in the exhaust stream, and if your engine has SCR, this will make it more efficient and reduce diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) consumption requirements.
Using a DOC also enables additional passive regeneration in DPF systems.
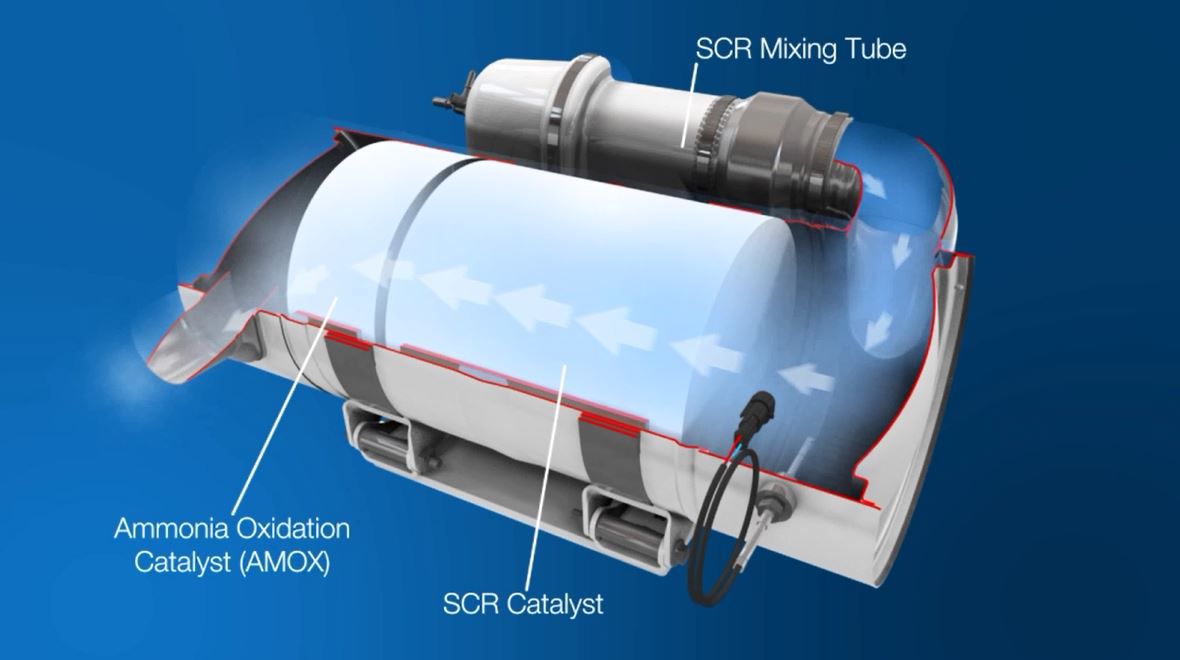
If you’re using a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system you need diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) for the system to work.
Learn MoreA diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) is an aftertreatment component that is designed to convert carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide and water.
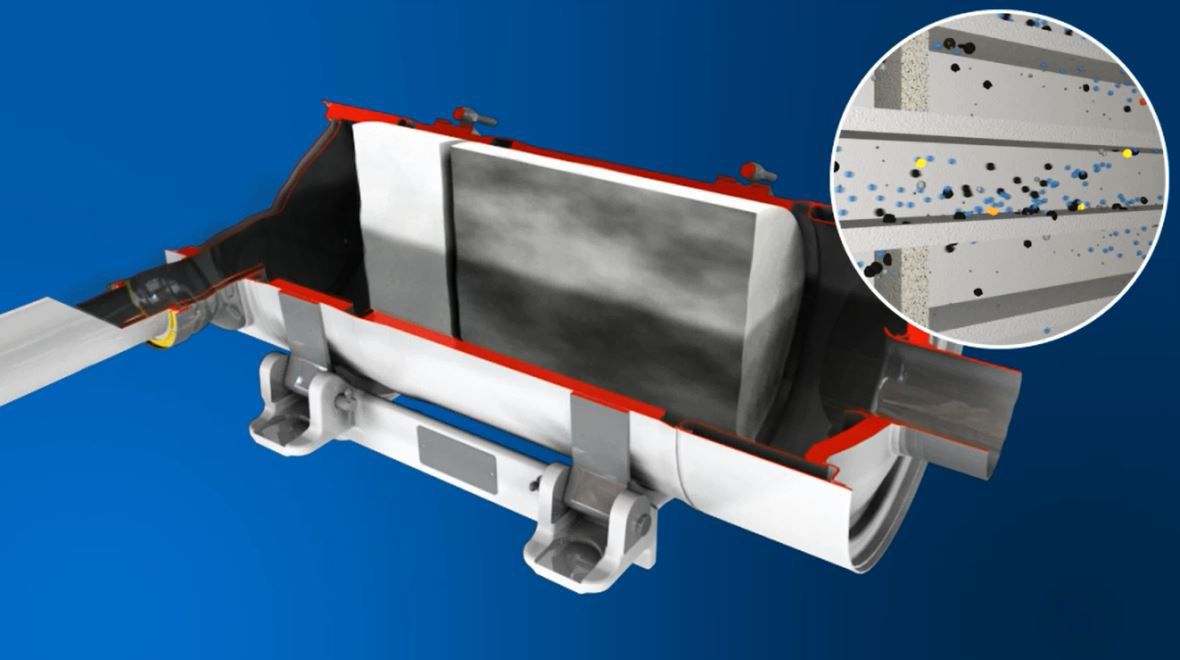
Learn MoreOur diesel particulate filter (DPF) solutions capture a high percentage of particulate matter or soot.
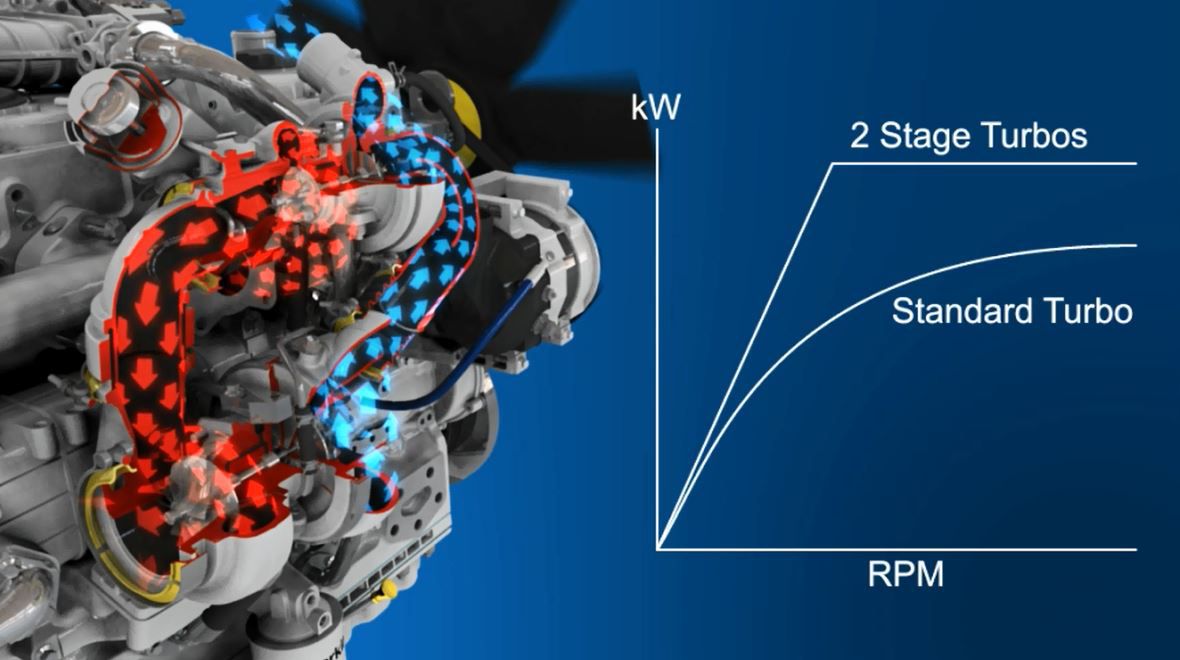
Learn MoreA series turbo set-up involves two turbochargers installed to operate in sequence.
Learn MorePassive regeneration is an approach used to oxidise particulate matter (PM) in the diesel particulate filter (DPF).
Learn MoreOne of the options available for reducing NOx emissions is selective catalytic reduction (SCR), used on a number of our engines.
Learn MoreOne of the technologies available for the reduction of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) is exhaust gas recirculation (EGR).
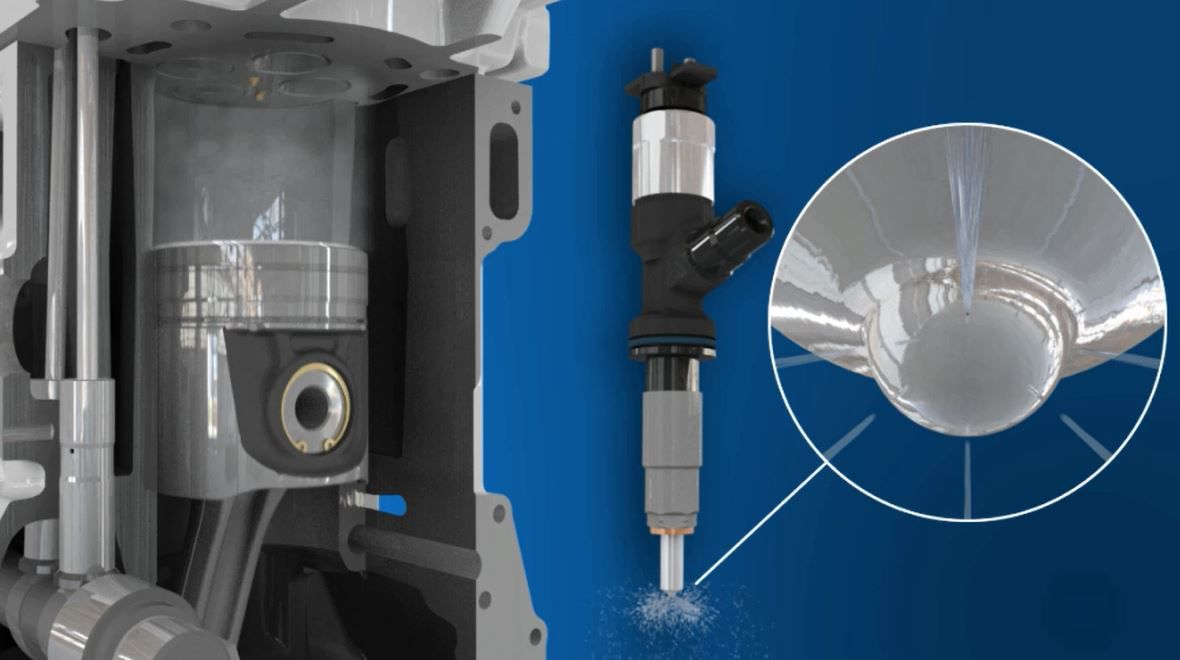
Learn MoreReducing particulates and optimising fuel consumption are primary reasons for adding high pressure common rail to our engines.
Learn MoreIf you're ready to receive trusted advice from a Perkins expert, speak to our team today.
Connect with usOur digital magazine with the latest news, interviews and analysis.
Read moreYour regional Perkins Distributor can provide local, on-the-ground engine support.
Learn More